Search
Search for projects by name
 Paradex
Paradex
Badges
About
Paradex is a high-performance crypto-derivatives exchange offering zero fee and private perpetuals.
Badges
About
Paradex is a high-performance crypto-derivatives exchange offering zero fee and private perpetuals.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a sufficiently decentralized data availability committee rely on few entities to safely attest data availability on Ethereum. A small set of entities can collude with the proposer to finalize an unavailable state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Jan 01 — 2026 Jan 01
This section shows how much data the project publishes to its data-availability (DA) layer over time. The project currently posts data to![]() Ethereum.
Ethereum.
2025 Jan 02 — 2026 Jan 01
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Paradex introduces privacy perps
2025 Dec 15th
Paradex introduces a privacy council to manage decryption keys for encrypted data availability.
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be frozen if
Users can be censored if
MEV can be extracted if
There is no mechanism to have transactions be included if the sequencer is down or censoring.
STARKs are zero knowledge proofs that ensure state correctness.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Only the whitelisted proposers can publish state roots on L1, so in the event of failure the withdrawals are frozen.
Encrypted blobs via privacy council
Data is posted as encrypted blobs on Ethereum using a random symmetric key per state update. Such symmetric key is also posted, but encrypted to the privacy council members public keys. Each member can recover the symmetric key and decrypt the data. The council has 3 members and at least one is required to disclose the decryption keys to reconstruct the L2 state. Users cannot independently reconstruct the L2 state without relying on the council members.
Funds can be frozen if no privacy council member discloses the decryption keys.
Paradex uses stateful compression since v0.13.4.
There is no non-empty genesis state.
The data format has been updated with different versions, and the full specification can be found here.
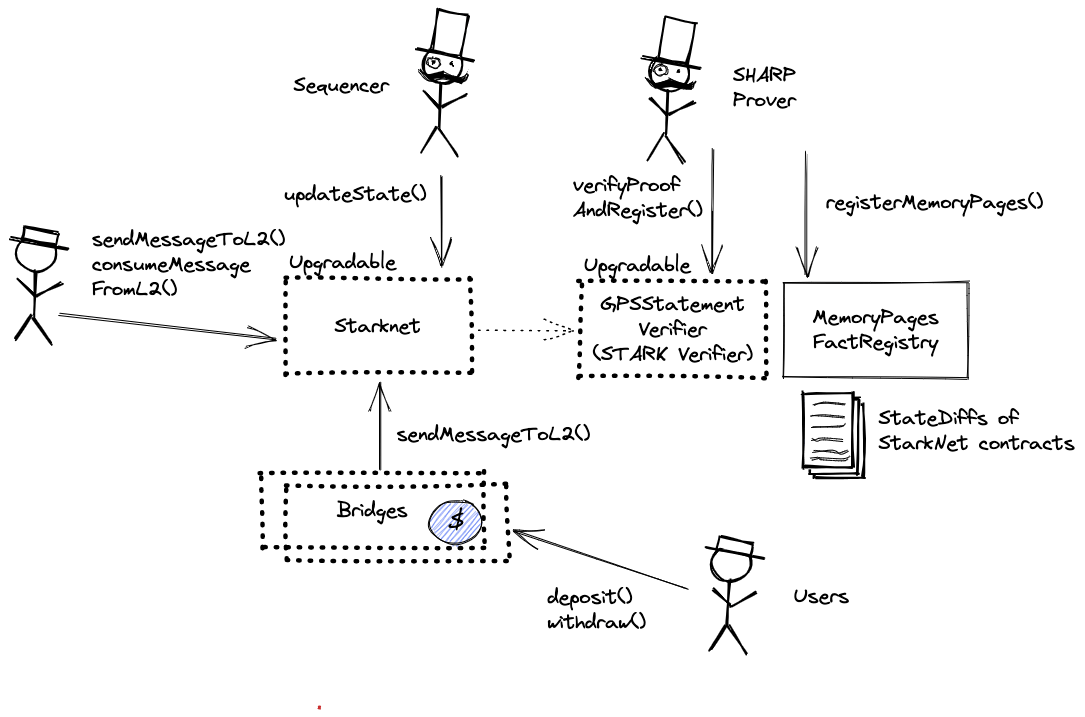
Each update to the system state must be accompanied by a ZK proof that ensures that the new state was derived by correctly applying a series of valid user transactions to the previous state. These proofs are then verified on Ethereum by a smart contract.
The system has a centralized operator
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can't force any transaction
There is no general mechanism to force the sequencer to include the transaction.
Users can be censored if the operator refuses to include their transactions.
Emergency exit
There is no generic escape hatch mechanism as Starknet cannot be forced by users into a frozen state. Note that a freezing mechanism on L2, to be secure, requires anti-censorship protection.
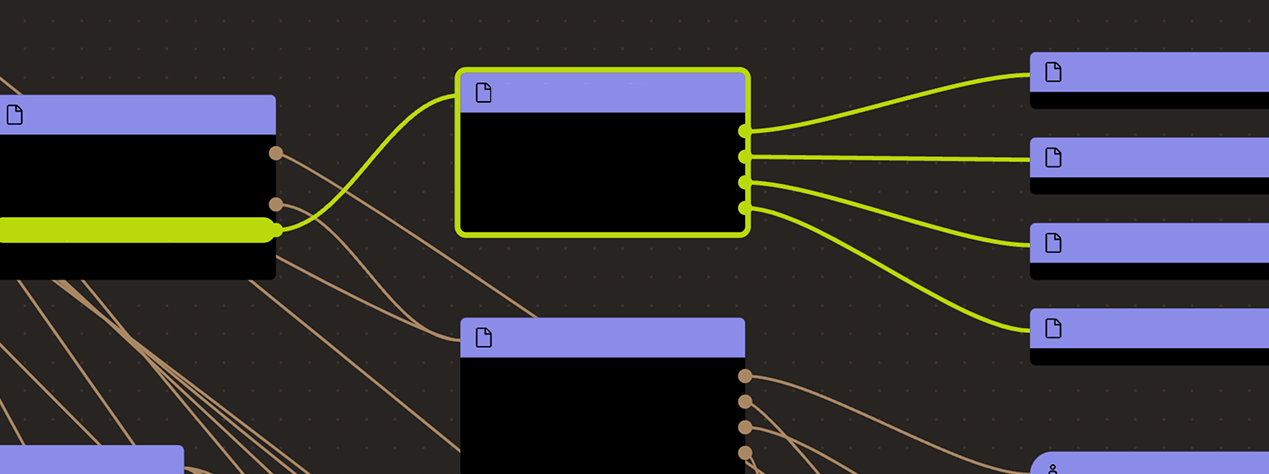
Ethereum
Roles:
Permissioned to regularly update the state of the L2 on L1. Each state update must have been proven via the SHARP verifier and contains state diffs for data availability.
Permissioned to manage the Operator role, finalize state and change critical parameters like the programHash, configHash, or message cancellation delay in the core contract.
Actors:
A Multisig with 2/4 threshold.
- Can upgrade with 8d delay
- SHARPVerifierCallProxy - acting directly with 8d delay
- Can interact with SHARPVerifierCallProxy
- manage the upgrade admin amd access control roles
- set custom implementations for specific operators (changes the verifier based on who calls it)
A Multisig with 2/5 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- Paradex
- A Governor - acting directly
A Multisig with 3/6 threshold.
- An Operator - acting directly

Ethereum
Upgradable call proxy contract through which the SHARPVerifier can be called. A call proxy does not delegatecall and the storage context remains at the target contract. It allows SHARP Multisig to change the otherwise immutable verifier contract with 8d delay.
- Roles:
- admin: SHARP Multisig
- appGovernor: SHARP Multisig
- governanceAdmin: SHARP Multisig
Shared Starkware SHARP verifier used collectively by Starknet and other SN stack and StarkEx projects. It receives STARK proofs from the Prover and verifies the integrity of the offchain execution including a correctly computed state root which is part of the Program Output.
Standard Starkware bridge escrow (single token). Withdrawals can be throttled to 0% of the locked funds per 24 hours.
- Roles:
- admin: Paradex Multisig 2
- govAdmin: Paradex Multisig 2
- secAdmin: Paradex Multisig 2
- secAgent: Paradex Multisig 2
- This contract stores the following tokens: USDC.
Auxiliary to the SHARPVerifier contract: Verified ‘memory fact pages’ get stored here. This is important as it registers all necessary onchain data produced by the verifier.
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Paradex USDC Escrow. The current bridge cap is 250 M USDC.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
